Understanding the Coronal Hole
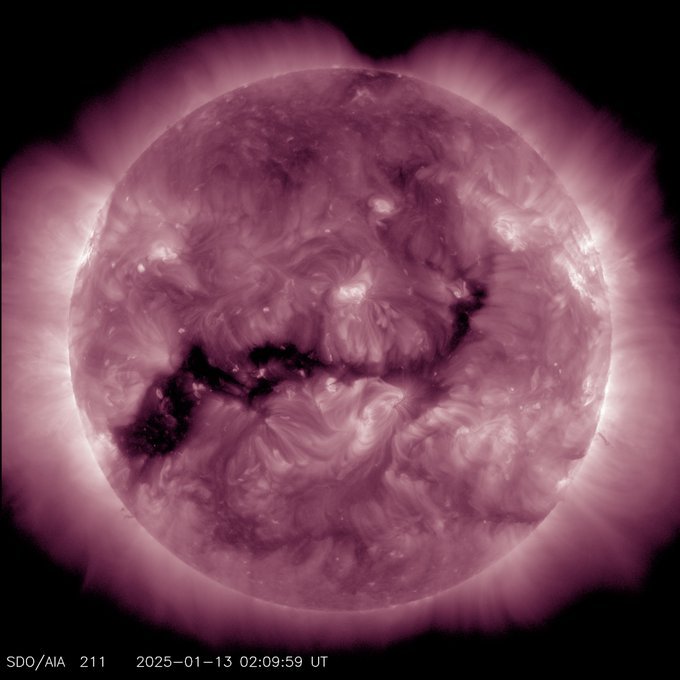
NASA’s recent observations reveal a massive coronal hole on the sun, which extends to approximately one-quarter of its circumference.
Coronal holes are regions where the sun’s magnetic field opens up, allowing solar winds to escape into space much more readily than through other areas of the sun’s surface.
This solar phenomenon has captured the attention of scientists and space enthusiasts alike.
Effects on Earth
As these unusually fast solar winds travel towards Earth, we can expect to see several effects. One of the most exhilarating outcomes is the enhancement of auroral displays.
Auroras, commonly known as the northern and southern lights, are a spectacular sight when solar winds interact with the Earth’s magnetic field.
Furthermore, there are concerns about possible disruptions to satellite communications and power grids due to these solar events.
While some discussions online include humorous takes and exaggerated concerns, expert opinions suggest that such occurrences are relatively common and rarely catastrophic.
What to Expect Next
As we anticipate the arrival of these solar winds within days, it’s worth noting that many have taken to social media to share their insights and concerns.
Discussions range from scientific observations to lighthearted anecdotes, creating a diverse conversation around this celestial phenomenon.
For those intrigued by solar activity, staying informed through reputable sources can enhance our understanding and appreciation of the sun’s dynamic behavior.
The Distance of the Sun from Earth: Understanding Our Cosmic Balance
The distance from the Sun to Earth is a topic that fascinates both astronomers and casual sky watchers alike.
This distance is not just a number; it plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the Earth’s environment, including its magnetic fields.
On average, the distance from the Sun to Earth is The measurement is known as an Astronomical Unit (AU) and serves as a cornerstone for astronomical calculations.
At this distance, the Sun’s gravitational pull is balanced by the Earth’s own gravitational forces, creating a stable orbit that allows life to thrive.
The Earth’s distance from the Sun is precisely what creates the unique conditions necessary for sustaining life.
The gravitational interaction between the Sun and Earth balances the planet’s magnetic fields, resulting in a protective shield against cosmic radiation.
If this distance were to change dramatically, the delicate balance we depend on could easily be disrupted, leading to unforeseen consequences.
In essence, the distance between the Sun and Earth is more than mere statistics; it is a fundamental aspect of our planet’s ecological and magnetic stability.
Understanding this cosmic relationship allows us to appreciate the intricate balance that governs our existence in the universe.